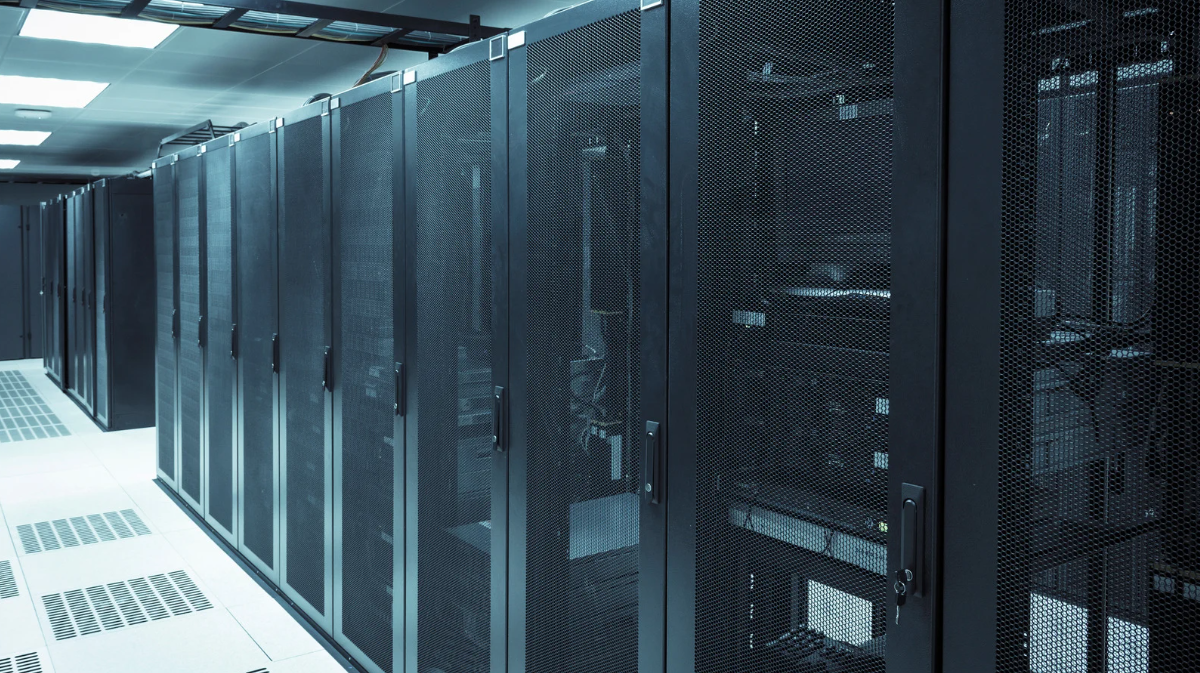
Data centers are critical infrastructure in today’s digital economy, serving as the backbone of cloud computing, online services, enterprise applications, and large-scale data processing. These facilities are meticulously designed to ensure high availability, scalability, and security, supporting continuous digital operations across multiple sectors. Understanding what is inside a data center is essential for IT professionals, business leaders, and technology stakeholders seeking insight into the architecture that powers modern information systems.
This article provides an in-depth examination of the key components and operational systems within a data center, highlighting how each contributes to performance, reliability, and security.
What Is Inside a Data Center?
A data center is the backbone of modern digital operations, housing the critical infrastructure that stores, processes, and transmits data around the clock. Inside, carefully engineered systems work together to ensure performance, security, reliability, and uninterrupted uptime.
1. Core Computing Infrastructure: Servers
At the center of every data center are servers, specialized computing devices responsible for processing, storing, and delivering data. Servers handle a wide range of applications, from hosting websites and databases to running enterprise software and cloud services.
Data centers typically utilize several server types:
- Rack Servers – Standardized, modular servers mounted in racks to maximize space utilization and operational efficiency.
- Blade Servers – High-density, modular servers that optimize computing power while minimizing footprint.
- Tower Servers – Standalone servers that provide dedicated computing resources for specific workloads.
Servers are arranged in racks and rows, forming a structured environment that facilitates airflow management and efficient maintenance. To ensure continuous operation, data centers implement redundancy and load balancing, enabling alternate servers to assume workloads in the event of failure.
Professional Insight: Servers represent the computational core of a data center, providing the processing capacity necessary for enterprise operations and cloud services.
2. Networking Infrastructure
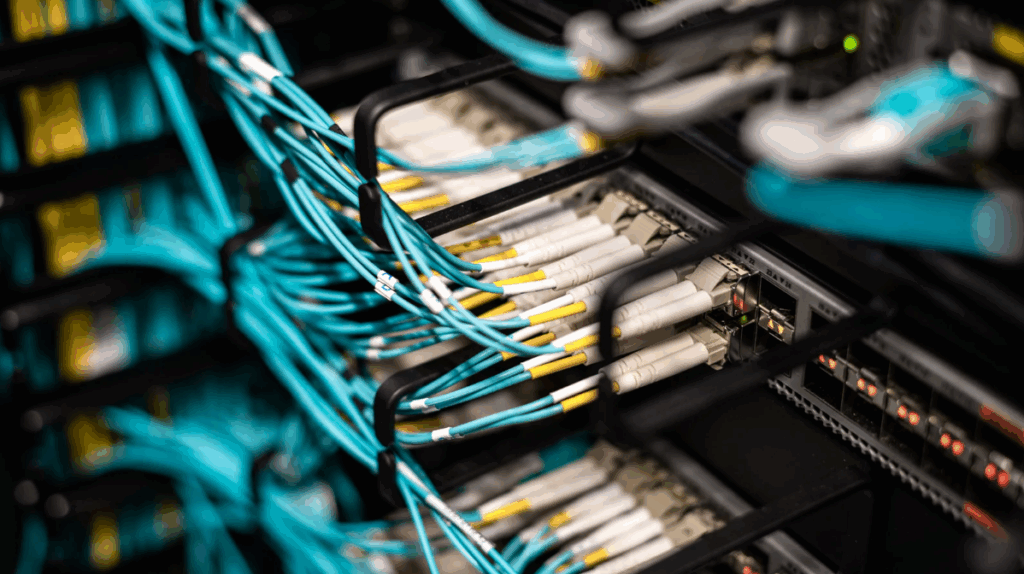

A robust networking infrastructure is fundamental to data center operations, facilitating the rapid and secure transfer of information across servers, storage systems, and external networks.
Key networking components include:
- Switches – Direct data traffic within the data center to optimize throughput.
- Routers – Connect internal networks to external systems and the internet.
- Firewalls – Provide cybersecurity protection against unauthorized access.
- Structured Cabling – Fiber optic and copper cabling ensure reliable and high-speed connectivity.
Network architecture is designed with redundancy and failover mechanisms, ensuring uninterrupted operations and minimal latency. Properly configured networking infrastructure is essential for meeting the performance and reliability expectations of enterprise applications.
Professional Insight: Networking equipment functions as the data center’s circulatory system, enabling efficient data flow and connectivity for mission-critical workloads.
3. Power Systems and Backup Solutions
Data centers demand high levels of electrical power to operate servers, networking devices, and environmental control systems. Reliable power infrastructure is critical for operational continuity and service level agreements (SLAs).
Key components of data center power systems include:
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) – Provides immediate backup power during primary power disruptions.
- Backup Generators – Sustain operations during extended power outages.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs) – Deliver electricity safely and efficiently to equipment.
Data centers incorporate redundant power systems to minimize the risk of downtime. Many facilities also integrate energy-efficient solutions, such as renewable energy sources and optimized power usage, to reduce environmental impact and operational costs.
Professional Insight: Power systems are the operational backbone of a data center, ensuring uninterrupted availability and reliability for critical workloads.
4. Cooling and Environmental Control
Servers generate substantial heat during operation, making cooling systems essential for maintaining optimal performance and extending equipment lifespan. Data centers employ advanced environmental control strategies to prevent overheating.
Common cooling methods include:
- CRAC Units (Computer Room Air Conditioning) – Regulate temperature and humidity in server rooms.
- Liquid Cooling Solutions – Provide high-efficiency heat removal directly from high-performance server components.
- Hot/Cold Aisle Containment – Segregates airflow to maximize cooling efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Continuous monitoring of environmental conditions ensures compliance with operational thresholds, preventing thermal-related failures and maintaining system reliability.
Professional Insight: Effective climate control is a critical component of operational integrity, ensuring that servers function within specified thermal parameters.
5. Data Storage Systems
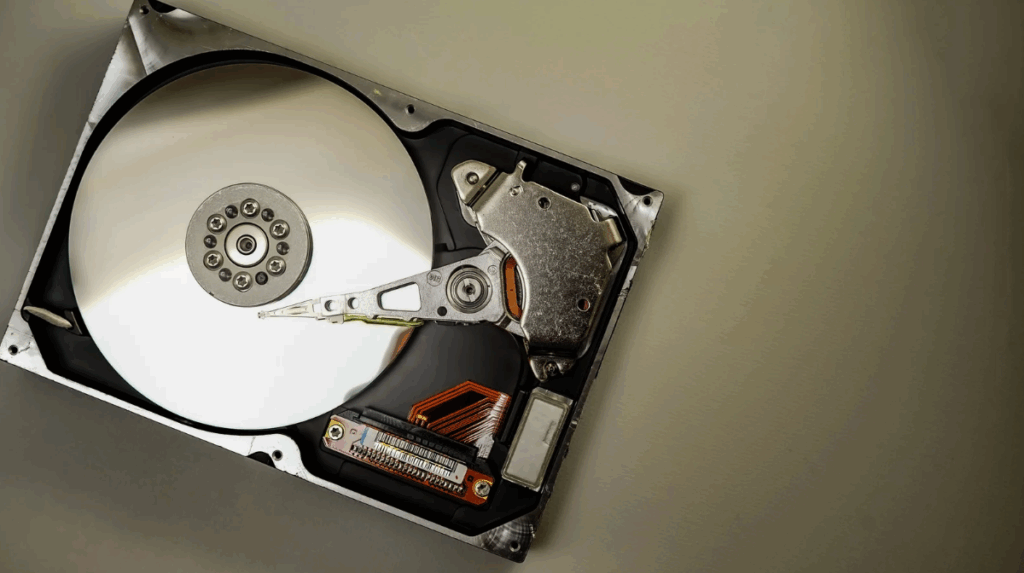

Data storage is a core function of any data center, enabling the retention, retrieval, and management of vast volumes of digital information.
Storage solutions include:
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) – Provide high-capacity, cost-effective storage for bulk data.
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs) – Deliver high-speed storage for performance-sensitive workloads.
- SAN (Storage Area Networks) – Centralized, high-performance storage accessible across multiple servers.
- NAS (Network Attached Storage) – Network-accessible storage solutions for shared data access.
Data centers implement redundancy protocols, such as RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), to safeguard against data loss and ensure high availability. Storage infrastructure underpins applications ranging from cloud computing and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to big data analytics.
Professional Insight: Data storage systems are the repository for enterprise knowledge and digital assets, supporting the operational, analytical, and transactional needs of organizations.
6. Security Infrastructure
Security is a critical aspect of data center design, encompassing both physical and cybersecurity measures. Data centers must safeguard sensitive information, intellectual property, and mission-critical systems from unauthorized access or compromise.
Physical security measures:
- Biometric access control and keycard systems
- Surveillance cameras and 24/7 security personnel
- Secured perimeters and locked server cages
Cybersecurity measures:
- Firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems
- Data encryption and access control policies
- Tiered security architecture for defense-in-depth
Professional Insight: Data centers function as secure operational hubs, implementing comprehensive measures to mitigate physical and digital threats while maintaining compliance with industry standards.
7. Monitoring and Management Systems
Effective data center operations require continuous oversight. Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) systems provide real-time monitoring, analytics, and management capabilities.
DCIM solutions monitor:
- Power usage and energy efficiency metrics
- Server and storage performance
- Environmental conditions, including temperature and humidity
- Network traffic and bandwidth utilization
Automation and predictive analytics help identify potential issues before they impact operations, supporting proactive maintenance and operational efficiency.
Professional Insight: DCIM systems enable centralized, data-driven management, ensuring operational excellence and adherence to performance benchmarks.
8. Redundancy and Disaster Recovery

Data centers must ensure continuous availability, even in the event of equipment failures, natural disasters, or cyber incidents.
Key strategies include:
- Redundant power and network systems
- Failover servers and disaster recovery sites
- Offsite and cloud-based backup solutions
High-availability architectures minimize downtime and support business continuity objectives, critical for enterprises relying on 24/7 digital services.
Professional Insight: Redundancy and disaster recovery planning are integral to resilient data center operations, safeguarding critical business functions against disruption.
9. Personnel and Operations
Although data centers employ advanced automation, skilled personnel remain essential to operational integrity. Teams include:
- Network Engineers – Maintain connectivity and optimize network performance.
- System Administrators – Manage servers, storage, and software environments.
- Security Specialists – Oversee physical and digital security protocols.
- Facilities Managers – Maintain environmental control, power, and structural systems.
Professional management ensures compliance with operational standards, security protocols, and performance objectives, supporting the reliable delivery of IT services.
Professional Insight: Data center personnel provide critical expertise, enabling the integration of technology, infrastructure, and operational practices.
10. Emerging Trends in Data Centers
Data centers are evolving rapidly to accommodate increasing demand, technological advancement, and sustainability imperatives. Emerging trends include:
- Edge Computing – Deploying smaller, localized data centers to reduce latency and improve responsiveness.
- AI-Driven Management – Utilizing artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance, resource allocation, and operational optimization.
- Sustainable Operations – Implementing renewable energy sources, advanced cooling systems, and energy-efficient design principles.
These innovations reflect the ongoing transformation of data centers into more intelligent, sustainable, and agile infrastructure.
Professional Insight: The future of data centers emphasizes efficiency, resilience, and adaptability to meet the demands of an increasingly digital global economy.
Conclusion
Data centers are complex facilities comprising servers, networking equipment, storage systems, power and cooling infrastructure, security measures, monitoring tools, and highly skilled personnel. Each component is meticulously designed to ensure high availability, reliability, and security, supporting the digital operations that drive modern business and society.
We hope this article has helped you gain a clearer understanding of what is inside a data center and how each element contributes to its overall functionality. If you have more questions about data centers, their components, or how they support modern IT and cloud services, please feel free to reach out to Efficient Lowvolt Solutions or explore additional resources to deepen your knowledge.

